1. 概要
和 Android 类似, WPF中也有很多内置的 UI组件, 且比Android的内置组件还要丰富. 如:
Button, Lable, TextBox, Menu, ListBox等等.
同样类似的还有, Android中可以使用 Activity, Fragment 放置这些 UI组件, 在WPF中 可以使用 Window , Page 放置UI组件. 用户通过Window 与 APP进行交互.
2. Window的外观
用户通过windows 与WPF 应用程序交互. 在WPF中 , windows 由 Window类封装. 该类支持:
- 创建和显示窗口
- 建立所有者/所拥有窗口的关系(Owner)
- 配置窗口的外观
- 对窗口生存期进行跟踪并与之交互
2.1 Window的外观组成
下图是 Window的基本组成:

Window 分为两个区域: 非工作区(Non-Client Area) 和 工作区(Client Area).
其中的 非工作区 是由 WPF 实现的, 包括 大多数 Window 共有的部分, 包括:
- Border : 边框
- Title : 标题
- Icon : 图标
- Minimize, Maximize, Restore Button: 最小化, 最大化, 还原 按钮
- Close Button : 关闭按钮
- System Menu : 系统菜单
- Resize Grip : 调整大小拖动块
工作区 是 非工作区内部的区域, 由开发人员自己决定显示内容.
2.2 Window的实现
类似于 Android的 Activity 一般由 Activity 子类 + XML 布局, WPF 中的 Window 也一般由 Window的子类 + XAML 布局文件组成.
XAML中实现一般的外观配置:
<Window x:Class="WindowDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WindowDemo"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<Grid>
</Grid>
</Window>在 Window的子类中实现一些逻辑处理:
namespace WindowDemo {
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for MainWindow.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class MainWindow : Window {
public MainWindow() {
InitializeComponent();
}
}
}2.3 Window外观配置
上述的 XAML 代码中 Grid 及包裹的部分为工作区域. Window 的外观配置如下
- Border
BorderBrush="Aqua" //边框颜色
BorderThickness="20" //边框宽度- Title 和 Icon
Title="MainWindow"
Icon="App.png"- Minimize, Maximize, Restore Button, Resize Grip
ResizeMode="xxx" // 控制可变大小
ResizeMode="CanMinimize" // 可最小化 不可最大化
ResizeMode="CanResize" // 可最大化 可最小化
ResizeMode="CanResizeWithGrip" // 可用 ResizeGrip 调整大小, 同时也可最大最小化
ResizeMode="NoResize" //不可调整大小- System Menu
ContextMenu="xxx"代码调整如下:
<Window x:Class="WindowDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WindowDemo"
mc:Ignorable="d"
BorderBrush="Red" BorderThickness="3"
ResizeMode="NoResize"
Title="Home" Icon="App.png"
Height="450" Width="800">
<Grid>
</Grid>
</Window>运行效果如下:
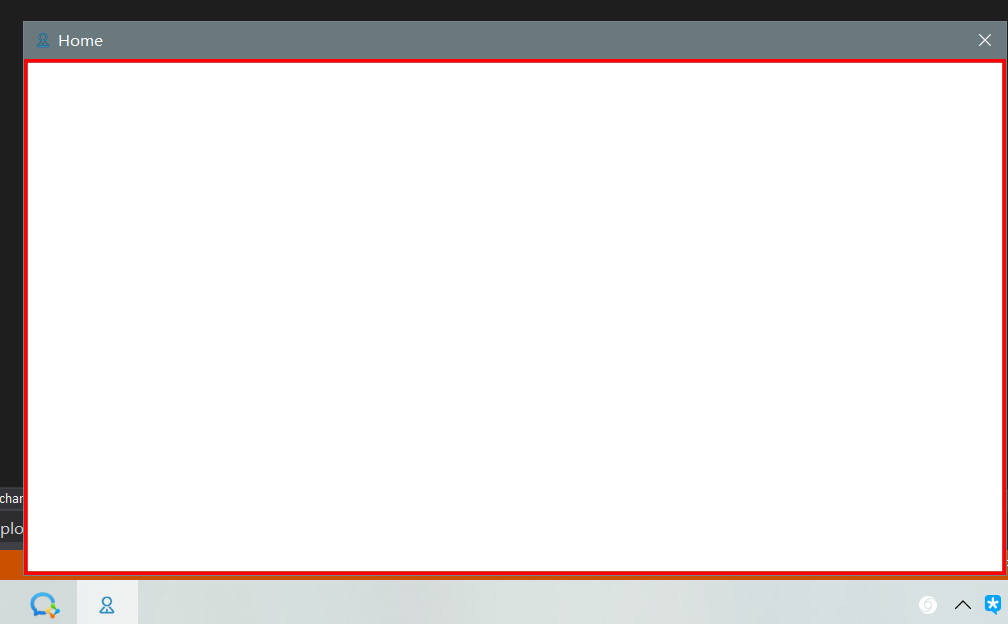
从上图可见, Icon 控制着 标题栏的图标 和 任务栏的图标.
上图是 ResizeMode="NoResize" 的效果, 其他不同的 ResizeMode 效果图如下:



如果不设置 ResizeMode 则默认和 CanResize 效果一致.
2.4 Window 的其他常用属性
1. AllowsTransparency
含义: 是否允许工作区域背景为透明, 此属性要求不适用WPF自己的WindowStyle, 必须将WindowStyle设置为None, 否则会抛出 InvalidOperationException异常.
此属性作用在于如果 工作区域小于 Window时, 中间区域是否允许透明. 例如工作区域设置圆角:
<Window x:Class="WindowDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WindowDemo"
mc:Ignorable="d"
WindowStartupLocation="CenterScreen"
BorderBrush="Red" BorderThickness="3"
WindowStyle="None"
ResizeMode="CanResize"
Title="Home" Icon="App.png"
Height="450" Width="800">
<Border CornerRadius="50" Background="Aqua">
</Border>
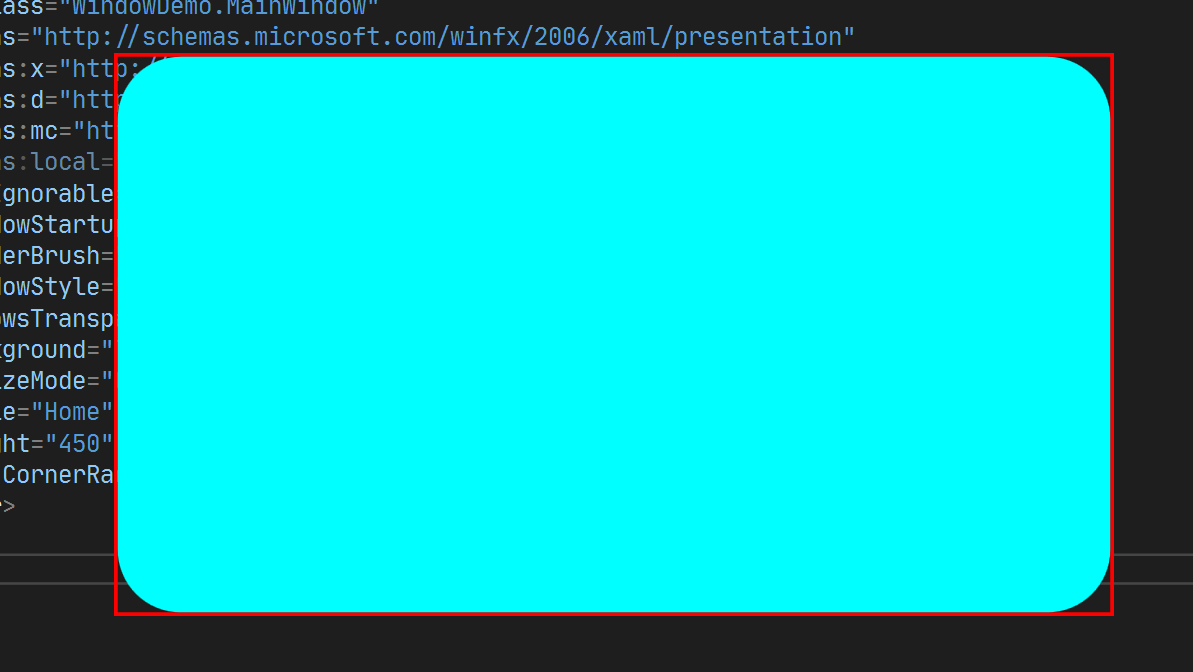
</Window>上述代码没有设置 AllowsTransparency , 运行效果如下:

设置AllowsTransparency="True"以后, 顶部的一个边 会消失.

四角的白色为 Window的 Background设置的颜色. 如果想去掉白色, 则需要设置 Window 的 Background 为 透明, 即: Background="Transparent", 此时从四角是可以看到下一层的Window内容.
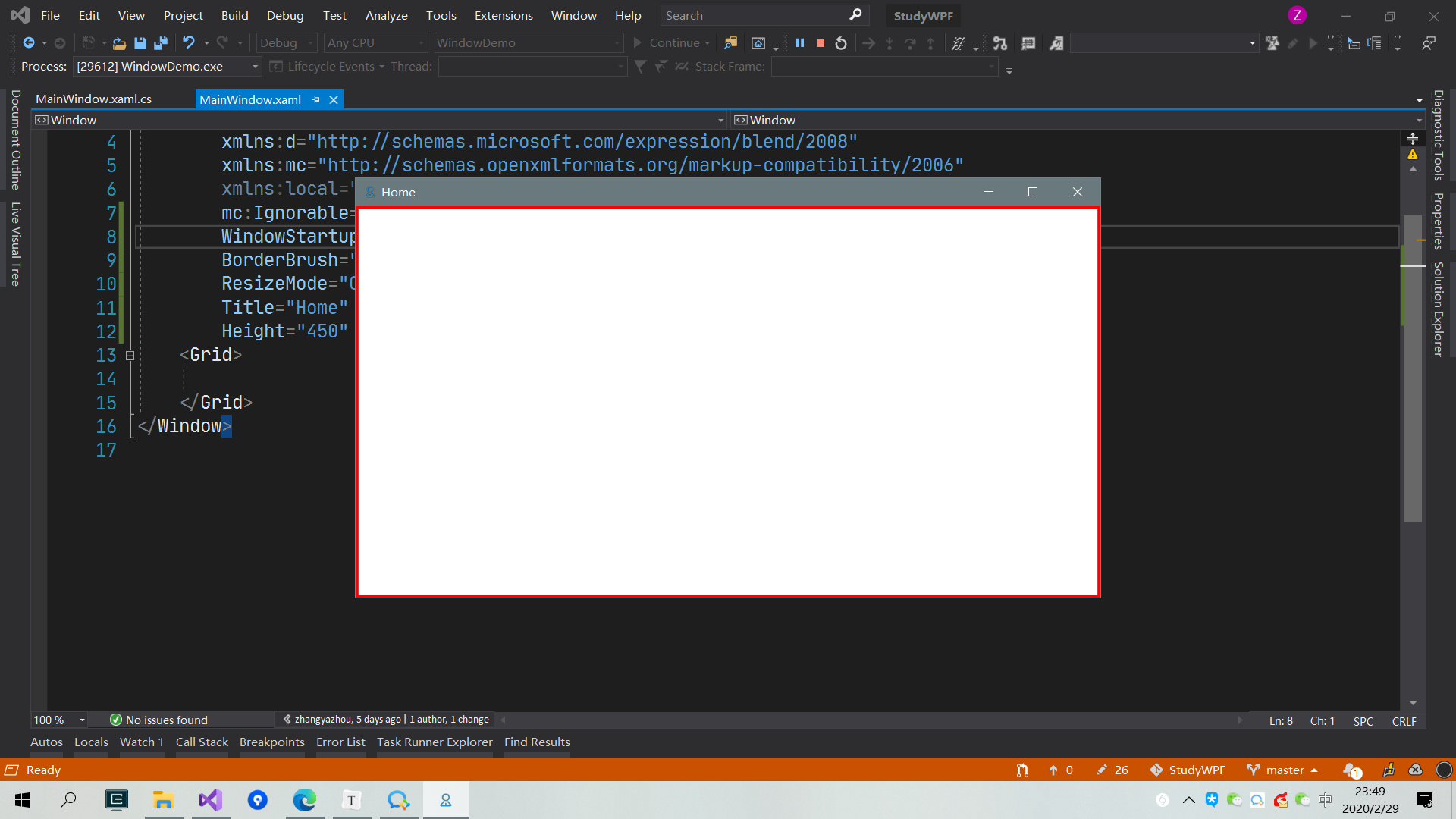
2. WindowStartupLocation
Window启动时的位置, 可选值为:
- CenterScreen : 在屏幕的中心
- CenterOwner : 在Owner Window 的中心
- Manual : 窗口根据其 Left 和 Top 属性值定位。 如果未指定 Left 或 Top 属性,则其值由 Windows 决定。
下图为 CenterScreen的效果:
3. ShowInTaskbar
该属性控制是否在任务栏显示图标, 如果设置为 False 则不会在 任务栏看到图标, 如果这时候最小化了Window ,则会在左下角显示一个小的控制条, 如下图:
点击还原按钮则可还原窗口.
4. ShowActivated
该值指示在第一次显示窗口时,窗口是否处于激活状态, 如果设置为 False, 效果如下:
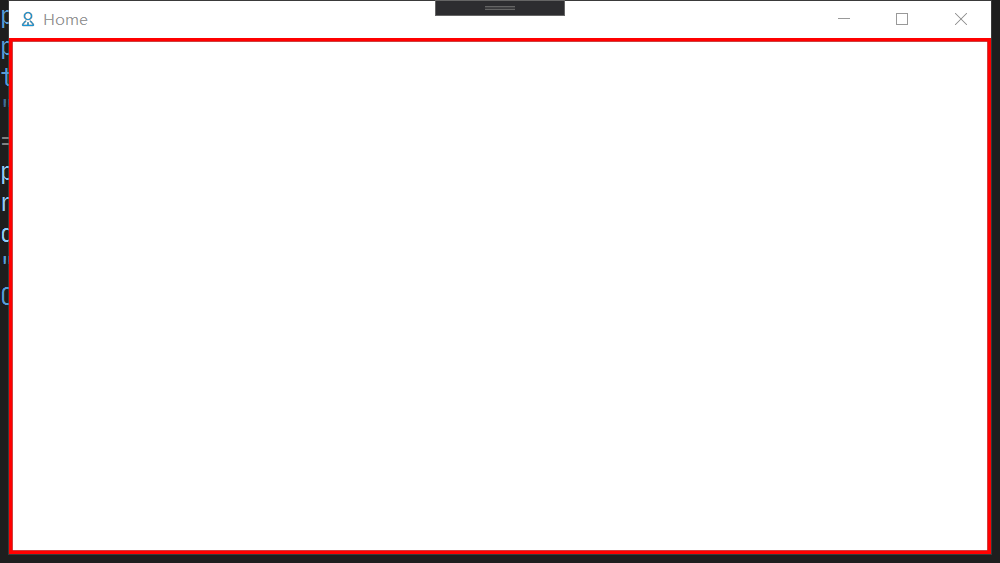
注意上图的标题栏背景的颜色是 未激活状态的 颜色.
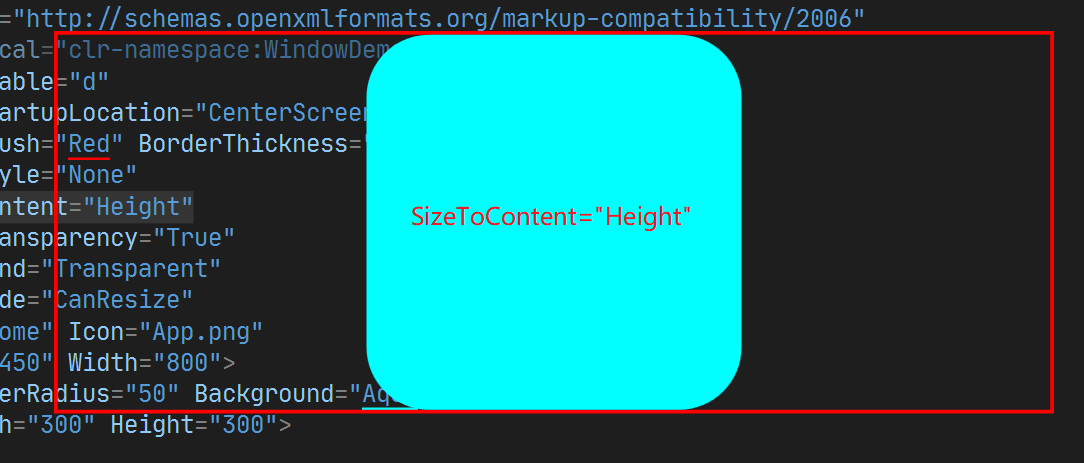
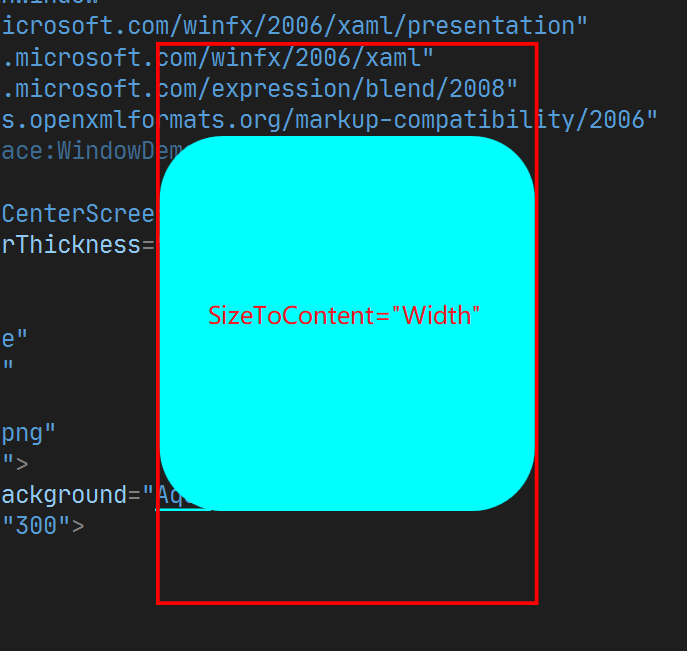
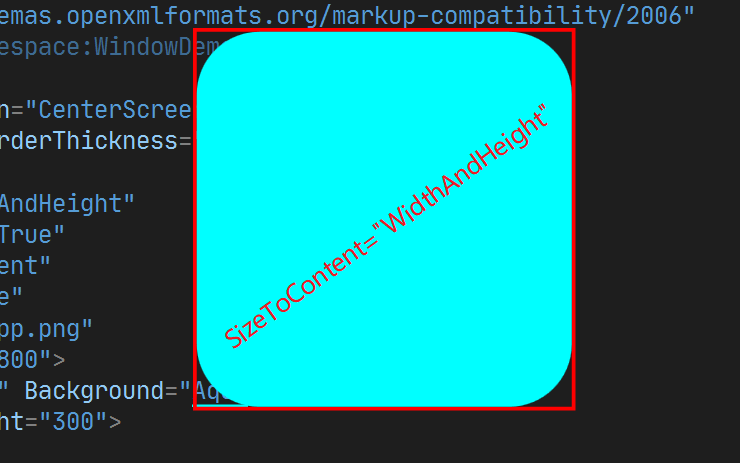
5. SizeToContent
含义: 设置窗口是否自动调整大小. 其可选值为:
- Height : 根据高度调整
- Width : 根据宽度调整
- WidthAndHeight: 同时调整宽度和高度
- Manual : 不调整
设置为 True 时, 如果工作区的实际大小没有Window 大小, 则会自动调整.
例如, 布局代码如下:
<Window x:Class="WindowDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WindowDemo"
mc:Ignorable="d"
WindowStartupLocation="CenterScreen"
BorderBrush="Red" BorderThickness="3"
WindowStyle="None"
AllowsTransparency="True"
Background="Transparent"
ResizeMode="CanResize"
Title="Home" Icon="App.png"
Height="450" Width="800">
<Border CornerRadius="50" Background="Aqua"
Width="300" Height="300">
</Border>
</Window>此时没有设置 SizeToContent , 默认为 Manual 即 不调整大小.
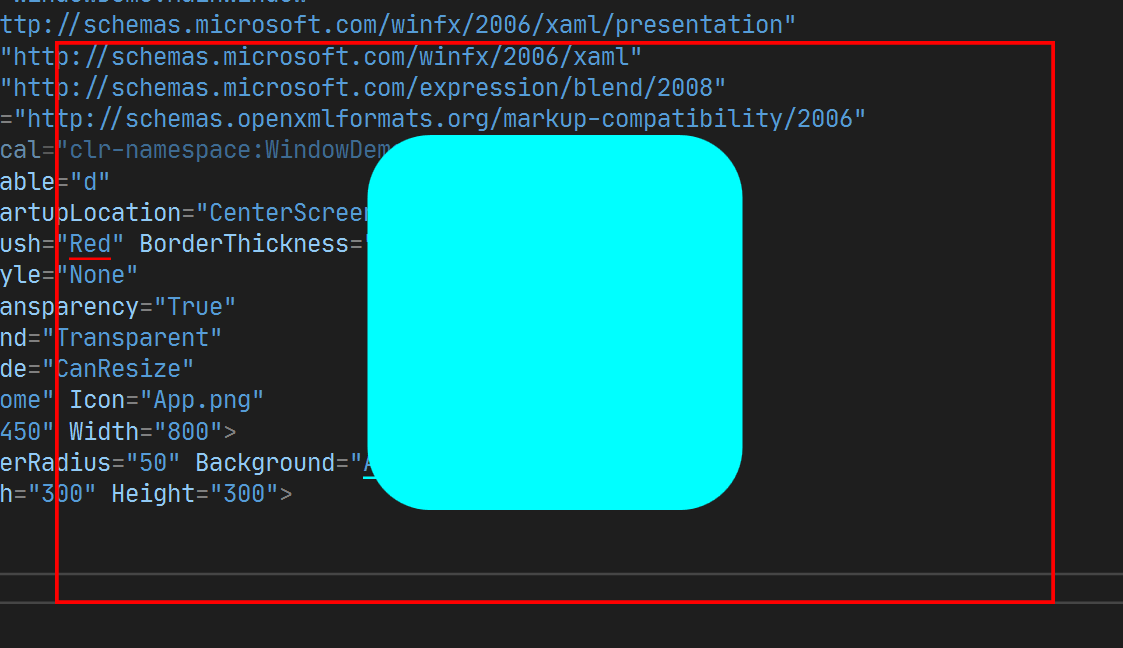
SizeToContent的其他的值效果如下:
6. Topmost
含义: 该值设置窗口是否出现在 Z 顺序的最顶层
Topmost 属性设置为 true 的窗口将显示在所有其 Topmos t属性设置为 false的窗口之上。
在将 Topmost 属性设置为 true的窗口组中,当前激活的窗口是最顶部的窗口。
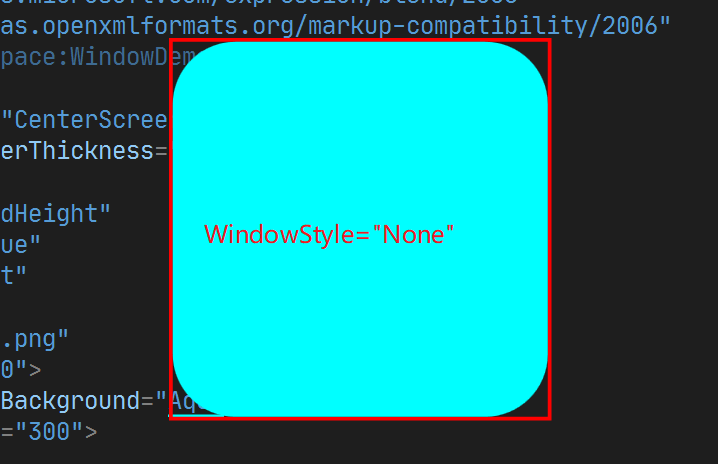
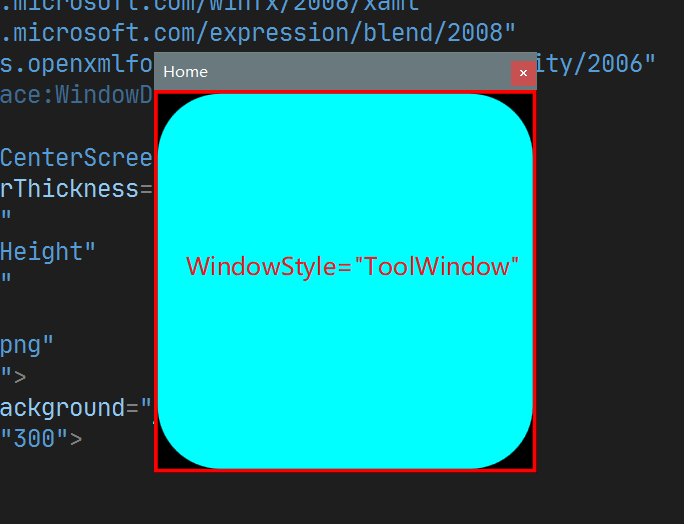
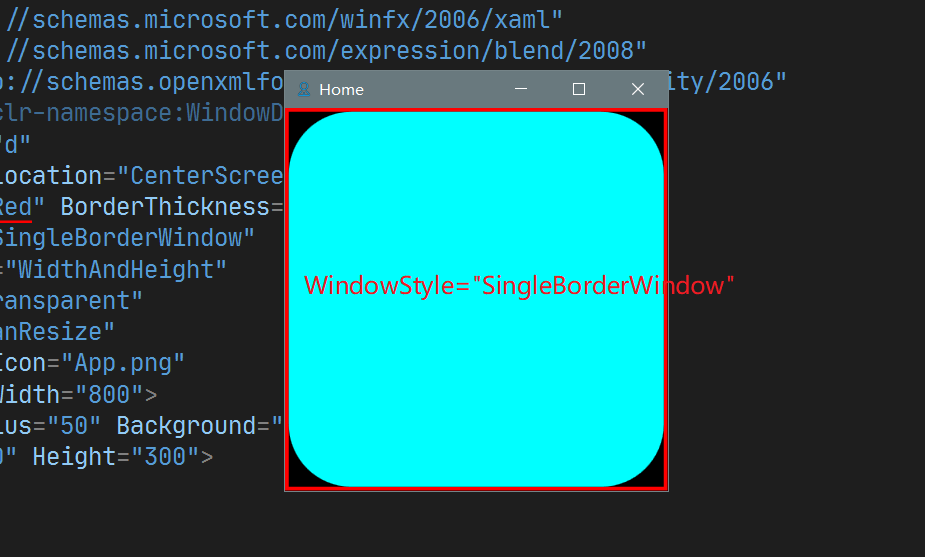
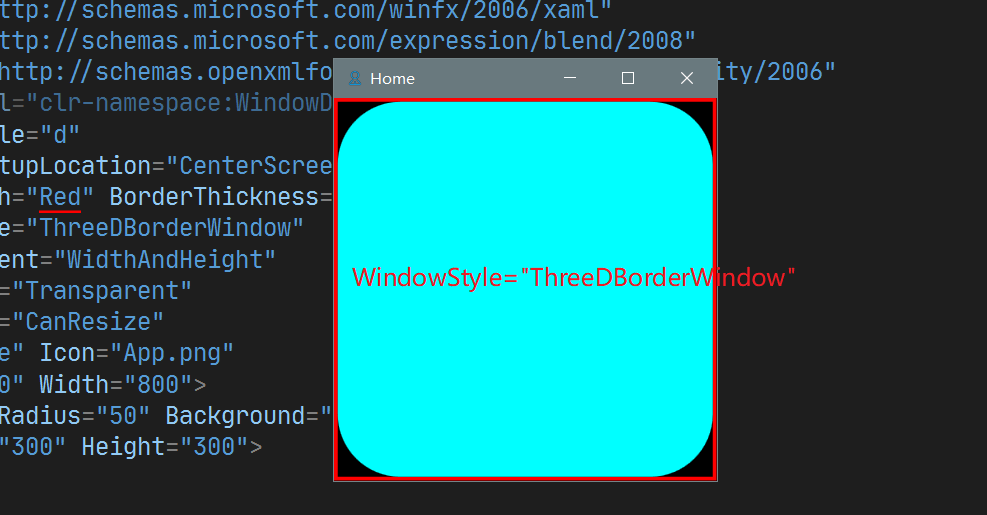
7. WindowStyle
设置 Window的风格, 类似于 Android Activity 的 theme设置. 其可选值有:
- None : 无Title bar区域
- SingleBorderWindow : 默认值, Title bar 包含 icon, title,及最大化最小化关闭按钮
- ThreeDBorderWindow : 3D边框风格
- ToolWindow : 无最大化最小化及Icon, 只有关闭按钮和Title
四种的效果如下:
布局
WPF的布局方式和Android的类似, 采用 XAML + cs 文件控制的形式.
0x01. WPF 布局原则
WPF的窗口只能包含单个元素, 如果在WPF 窗口中放置多个元素需要在窗口上添加个容器, 然后在容器中添加其他元素.
WPF 需遵循的布局原则如下:
- 不应显式设定元素的尺寸
- 不应使用屏幕坐标指定元素位置
- 布局容器的子元素共享可用的空间
- 可以嵌套布局容器
概括下来即: 不推荐使用绝对坐标布局, 布局中可以嵌套容器.
0x02. 布局过程
和Android 的布局过程不同的是, WPF的布局包括两个阶段:
- 测量(measure) 阶段
- 排列(arrange) 阶段
测量阶段是容器遍历所有的子元素,并获取子元素的期望尺寸.
排列阶段是容器在合适的位置放置子元素.
0x03. 布局容器
所有的WPF的布局容器的基类为 Panel (System.Windows.Controls) 抽象类面板, 此类的继承关系如下:
DispatcherObject
- DependencyObject
- Visual
- UIElement
- FrameworkElement
- Panel此外, Panel 类有三个重要的共有属性:
- Background : 面板的背景
- Children : 面板中存储的条目集合
- IsItemsHost : 用户显示与ItemsControl 控件关联的项, 非自定义面板一般不适用该属性.
常用的核心 Panel 的实现类有:
StackPanel: 类似于 Android 中的线性布局, 水平或者竖直排列子元素WrapPanel: 可换行的布局容器DockPanel: 根据容器的便捷调整元素的面板Grid: 表格布局UniformGrid: 强制所有单元格相同的表格布局Canvas: 绝对坐标布局的面板
除了核心面板外, Panel 还有很多专业的实现, 如下:
System.Windows.Controls.Canvas
System.Windows.Controls.DockPanel
System.Windows.Controls.Grid
System.Windows.Controls.StackPanel
System.Windows.Controls.VirtualizingPanel
System.Windows.Controls.WrapPanel
System.Windows.Controls.Primitives.TabPanel
System.Windows.Controls.Primitives.ToolBarOverflowPanel
System.Windows.Controls.Primitives.UniformGrid
System.Windows.Controls.Ribbon.Primitives.RibbonContextualTabGroupsPanel
System.Windows.Controls.Ribbon.Primitives.RibbonGalleryCategoriesPanel
System.Windows.Controls.Ribbon.Primitives.RibbonGalleryItemsPanel
System.Windows.Controls.Ribbon.Primitives.RibbonGroupItemsPanel
System.Windows.Controls.Ribbon.Primitives.RibbonQuickAccessToolBarOverflowPanel
System.Windows.Controls.Ribbon.Primitives.RibbonTabHeadersPanel
System.Windows.Controls.Ribbon.Primitives.RibbonTabsPanel
System.Windows.Controls.Ribbon.Primitives.RibbonTitlePanel1. StackPanel
StackPanel 默认为垂直排列布局, 用法如下:
<Window x:Class="WPFApp.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WPFApp"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" SizeToContent="WidthAndHeight" Width="200" Height="200">
<StackPanel>
<Button Content="Button1" Height="24"/>
<Button Content="Button2" Height="24"/>
<Button Content="Button3" Height="24"/>
<Button Content="Button4" Height="24"/>
</StackPanel>
</Window>如果更改 StackPanel 的方向为水平:
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal">
<Button Content="Button1" Height="24"/>
<Button Content="Button2" Height="24"/>
<Button Content="Button3" Height="24"/>
<Button Content="Button4" Height="24"/>
</StackPanel>StackPanel 有几个比较常用的 attribute 属性可在 xaml 中配置:
- HorizontalAlignment : 子元素的水平布局对齐方式, 类似Android的Gravity. 可选: Center, Left, Right, Stretch
- VerticalAlignment : 子元素的垂直布局对齐方式, 可选: Top, Center, Bottom, Stretch
- Margin : 面板外部的边距
- MinWidth, MinHeight: 面板的最小宽度和高度
- MaxWidth 和 MaxHeight : 面板的最大高度和宽度
- Width 和 Height : 面板的宽度和高度
2. WrapPanel
使用WrapPanel面板承载上面的四个按钮,
<Window x:Class="WPFDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WPFDemo"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="150" Width="200">
<WrapPanel>
<Button Content="Button1"></Button>
<Button Content="Button2"></Button>
<Button Content="Button3"></Button>
<Button Content="Button4"></Button>
</WrapPanel>
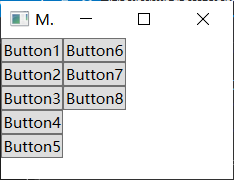
</Window>WrapPanel 和 StackPanel 类似, 默认布局方向会行, 可以手动修改为列:
<Window x:Class="WPFDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WPFDemo"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="150" Width="200">
<WrapPanel Orientation="Vertical">
<Button Content="Button1"></Button>
<Button Content="Button2"></Button>
<Button Content="Button3"></Button>
<Button Content="Button4"></Button>
<Button Content="Button5"></Button>
<Button Content="Button6"></Button>
<Button Content="Button7"></Button>
<Button Content="Button8"></Button>
</WrapPanel>
</Window>效果如下:
3. DockPanel
Dock 和 Mac 的 Dock工具栏类似 可以选择一个边停靠, DockPanel 的子元素也可以选择一个边停靠, 例如:
<Window x:Class="WPFDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WPFDemo"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="150" Width="200">
<DockPanel >
<Button Content="Button1" DockPanel.Dock="Left"></Button>
<Button Content="Button2" DockPanel.Dock="Top"></Button>
<Button Content="Button3" DockPanel.Dock="Right"></Button>
<Button Content="Button4" DockPanel.Dock="Bottom"></Button>
<Button Content="Button5"></Button>
</DockPanel>
</Window>4. Grid
Grid是最常用的也是最灵活的布局面板, 新建Window 默认的布局就是 Grid:
<Window x:Class="WPFDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WPFDemo"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="200" Width="200">
<Grid >
</Grid>
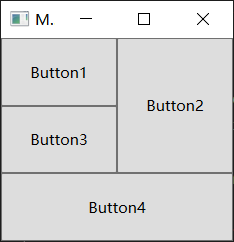
</Window>Grid 的缺省配置是 1行1列一个单元格. 如果要增加行和列,需要在 Grid 内部增加 Grid.ColumnDefinitions 和 Grid.RowDefinitions, 如下配置 2 x 3 的 Grid :
<Window x:Class="WPFDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WPFDemo"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="200" Width="200">
<Grid >
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition></ColumnDefinition>
<ColumnDefinition></ColumnDefinition>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition></RowDefinition>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Button Content="Button1" ></Button>
<Button Content="Button2" Grid.Column="1" Grid.RowSpan="2"></Button>
<Button Content="Button3" Grid.Row="1"></Button>
<Button Content="Button4" Grid.Row="2" Grid.ColumnSpan="2"></Button>
</Grid>
</Window>在 Grid的子元素中使用以下属性:
Grid.Row: 元素位置起始行, 从0开始, 默认为0Grid.Column元素位置的起始列, 从0开始, 默认为0Grid.RowSpan: 元素占用的行数, 默认为1Grid.ColumnSpan: 元素占用的列数, 默认为1
上述代码运行效果如下:
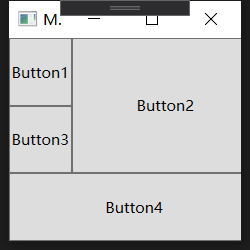
默认的行和列是均分, 可以手动设置行列尺寸, 如:
<Window x:Class="WPFDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WPFDemo"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="200" Width="200">
<Grid >
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="50"></ColumnDefinition>
<ColumnDefinition Width="150"></ColumnDefinition>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition></RowDefinition>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Button Content="Button1" ></Button>
<Button Content="Button2" Grid.Column="1" Grid.RowSpan="2"></Button>
<Button Content="Button3" Grid.Row="1"></Button>
<Button Content="Button4" Grid.Row="2" Grid.ColumnSpan="2"></Button>
</Grid>
</Window>运行效果如下:
类似于Android的百分比布局, Grid也可以按照比例设置每行的尺寸, 同样也可以添加分隔条:
<Window x:Class="WPFDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WPFDemo"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="200" Width="200">
<Grid >
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"></ColumnDefinition>
<ColumnDefinition Width="2*"></ColumnDefinition>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition></RowDefinition>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Button Content="Button1" ></Button>
<Button Content="Button2" Grid.Column="1" Grid.RowSpan="2"></Button>
<Button Content="Button3" Grid.Row="1"></Button>
<GridSplitter Grid.Row="2" ShowsPreview="True" Grid.ColumnSpan="2" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch" Height="1"/>
<Button Content="Button4" Grid.Row="3" Grid.ColumnSpan="2"></Button>
</Grid>
</Window>
运行效果如下:
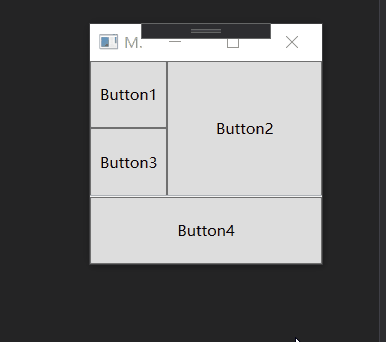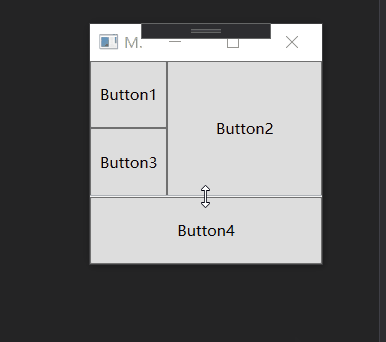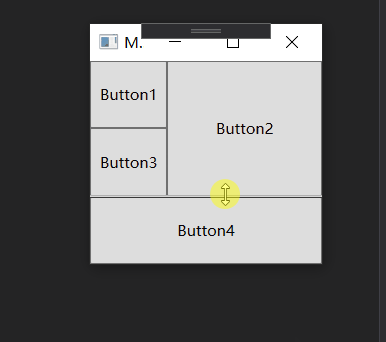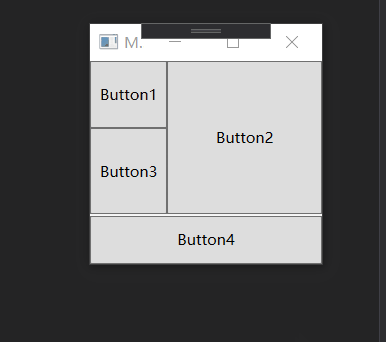
如果将上述的 ShowsPreview="True" 删除或者 改为 False 怎不会预览直接改变大小.




